Peru’s Growing Energy Market
Last month we began our examination of the growing energy market in Peru (Part One). We looked at the country’s expanding requirements for natural gas, their declining oil production, and their need for imports to meet the country’s demand. Part Two of this series continues exploring how their growing demand for LPG could impact the global propane markets.
Peru’s Growing Demand for LPG
Cooking and Heating
Peru’s main consumers of LPG are their commercial and residential sectors. The product is primarily used for cooking and heating. Demand for NGL in Peru’s LPG industry in 2020 stood at approximately 2 million tonnes. Forecasts indicate that this demand will reach 6.16 million tonnes by 2030. This increase represents a healthy annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 11.86%.
Autogas

Autogas is a viable fuel alternative in Peru, with filling stations widely distributed throughout the country. Users can access this fuel easily throughout the nation.
Another important source of LPG demand is the sector related to Autogas. Currently, there are more than 650,000 LPG-powered vehicles in Peru, both for private use and public service. This sector now represents 38% of the demand for LPG in the country, which totals more than 2 million tonnes per year.
Vehicle conversions to Autogas have been steadily increasing due to the growing preference for this cheaper alternative to gasoline and diesel fuels. Reasons for these conversions include significant consumer savings and environmental benefits. For example:
- A medium-sized car converted to Autogas can save the motorist around S/ 3,266 (soles) per year (approximately $980 USD).
- Pre-owned OEM LPG-powered vehicles with a 1.6-liter engine allow consumers to save up to S/ 3,266 (about $1,000 USD) annually in fuel costs.
- Autogas emits considerably less CO2 than gasoline or diesel.
- The use of LPG in Autogas translates into a significant reduction in the environmental footprint caused by vehicles.
Autogas represents a very widespread alternative in the country, with facilities and filling stations massively distributed throughout the nation. This allows users to access this fuel easily in many areas throughout the nation.
Government Initiatives Supporting Power Plant Conversions
Peru’s government promotes policies for economic growth by converting a significant number of power plants currently fueled by natural gas to LPG. These strong government initiatives to replace natural gas with LPG for power generation are expected to accelerate the growth of the LPG market in the country.
Imports – LPG (Propane and Butane)
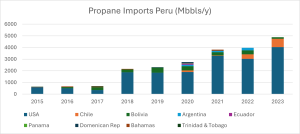
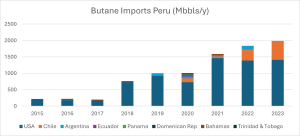
To meet domestic demand for LPG, Peru requires imports. These imports began in 2015 and continued to increase until this year. The largest supplier of LPG is the United States, providing 80% of the total received. Bolivia is the next largest supplier with 9.75% of the propane imports. Chile comes next with 5.85% of the propane imports and 12.3% of the butane imports. Other countries such as Argentina, Ecuador, the Dominican Republic, Bahamas, etc., have also provided LPG products, but with very low import value compared to the main suppliers.
These imports started with values of up to 820 Mbbls/year in 2015 to cover internal demand (specifically domestic use). As the population moves toward using domestic gas in a more intensive way, the requirements to cover these needs have increased. By 2023, less than a decade later, 6,868 MMbbls/year have been imported. This increase is reflected in the two graphs below.
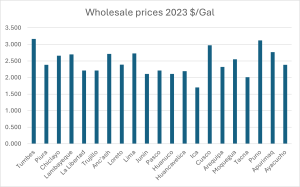
LPG Wholesale Prices
In the evaluation of the general sales prices, we noticed that they all interact at levels higher than those related to international trade (Mont Belvieu).
Peru’s Growing Energy Market
Conclusions
Peru’s LPG industry is growing steadily, driven by government initiatives, increasing demand and the adoption of Autogas. In 2012, the Peruvian government implemented rural fuel subsidies for low-income households to reduce health risks associated with household air pollution due to the use of dirty fuel for cooking such as kerosene or firewood. These subsidies have had excellent results. However, there is still room for growth in this program, as 82% of rural households still use solid fuels like firewood for cooking and heating.
Additionally, international prices make doing business in Peru more realistic. Latin American countries, like Peru, reference Mont Belvieu as a price benchmark, closely correlating local prices with global trends.
Autogas adoption in Peru has been driven by economic savings, environmental considerations, and the strategic expansion and promotion of the LPG refueling network.
Peru’s growing LPG market faces challenges related to production, increasing imports, and transitioning significant portions of its population to cleaner fuels. The Twin Feathers team continues to watch this growing market and will keep you up to date on global trends as well as local dynamics. As always, our goal is to provide you with expert advice that helps you make smart decisions every day.
“Your trusted advisors for energy markets.”