Chile – An Emerging Energy Market – Part Two
Last month we began our analysis of the emerging energy market in Chile (Part One). We examined the country’s growing demand for natural gas, their declining domestic production, and their substantial dependence on imports. We continue our exploration with Part Two of this post, looking at Chile’s energy market in greater detail and observing how the changes occurring could impact the global propane markets.
LPG Use in Chile
LPG is an important part of daily commercial and residential life in Chile. While most commonly used to fuel water heaters, stoves, and grills in Chilean homes, in recent years, there has been an increase in vehicles using LPG as a clean, economical fuel. Additionally, many industries depend on LPG to generate products and services. LPG use can be seen in the retail and hospitality sectors. Stores, restaurants, bars and other businesses use this fuel to provide warmth and service to their customers.
Internal Demand for LPG
The Chilean LPG market is relatively small on a global scale, representing 27 million metric tons per year, about 9% of global demand. However, the country’s LPG consumption has been steadily increasing. In 2022, the country’s average LPG consumption stood at 43.59 thousand barrels per day.
While Chile’s usage represents a relatively small portion of the global LPG market, it plays a crucial role in the country’s residential and commercial sectors. In fact, residential and commercial customers consume about 80% of the region’s LPG, which is significantly higher than the global average.
LPG Imports
Managing Imports
LPG imports in Chile are managed by companies specializing in this part of the energy market. The three largest importers are Gasmar, Hualpen and Oxiquim. These companies are the largest suppliers of LPG for Chile. They have developed sufficient infrastructure to receive VLGC (very large gas carrier) vessels and disperse the product.
LPG Infrastructure
Chile’s LPG infrastructure includes the Gasmar S.A. terminal and storage facility. Gasmar operates the Bahía Quintero facility, which is one of the largest LPG terminals on the Pacific coast of South America. The company primarily imports LPG from the United States through ocean carriers and stores it at their facilities. Additionally, Gasmar is expanding its operations by building a new terminal in Mejillones Bay. LPG plays a key role in displacing more carbon-intensive fuels, such as diesel and biomass, in Chile.
Main Suppliers of LPG
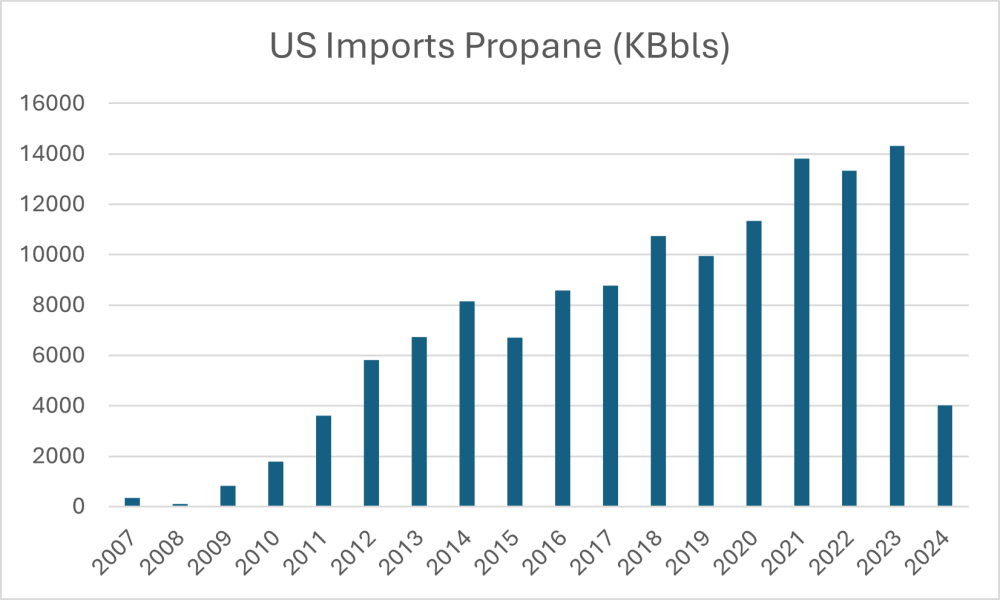
Since 2010, the United States has become the main supplier of LPG to Chile, maintaining significant volumes of gas to cover the country’s demand. Argentina also supplies LPG and LNG through pipelines, land transportation and in some cases by sea. These sources are crucial to meeting Chile’s energy needs, especially considering the country’s dependence on imported LPG.
The graph below illustrates Chile’s heavy reliance on LPG imports from the United States, averaging 135,000 tons per month (15 MMBbl/year) since 2010.
LPG Wholesale Prices
The LPG market in Latin America is influenced by the price indicators of the United States. Since the U.S. is the largest producer of propane, it generates this price marker in the region. When relating domestic sale prices in Chile, we see that these are highly influenced by global price movements and at a cost that is strongly dependent on imports. In the case of Chile, imports come mostly from the United States, which implies that the Mont Belvieu index is relevant and is normally used in internal cost and management definitions.
Chile’s Emerging Energy Market
Conclusions
Chile’s LPG market faces challenges due to its dependence on imports, lack of competitors, and sensitivity to global market dynamics. Efforts are being made to improve competition and regulate prices.
The demand for LPG is growing steadily in Chile. Residential and commercial use drives that demand, but recently Autogas use has increased as a clean, economical fuel option. Despite the lack of competitors, LPG consumption in Chile has increased by 80%. This increase has prompted efforts to improve market conditions through competition.
Chile has been largely dependent on the United States for LPG imports since 2010. However, since 2018, Argentina has been contributing by supplying LPG and LNG through pipelines.
Chile’s emerging LPG market is high in propane and the region’s overall demand is susceptible to global propane market movements. The country’s dependence on imports and sensitivity to global market dynamics make it an energy market to watch. The Twin Feathers team continues to observe this emerging market and will keep you informed on global developments as well as local changes. As always, our goal is to provide you with expert advice that helps you make smart decisions every day.
Chile – An Emerging Energy Market – Part Two
By Gabriel Amundarain